Radon Gas Testing During Home & Commercial Inspections in Tulsa
- Drew Sleezer
- 14 October, 2025
- CommercialResidential

When you’re buying a home or evaluating a commercial property in Tulsa, safety and investment value go hand in hand. While radon gas is a major concern in some parts of the country, Tulsa County and much of Oklahoma are classified as lower-risk areas. Still, radon varies property by property, which makes testing an important step in due diligence.
This guide walks through the facts: what radon is, what the data shows in Tulsa, how testing works, what results mean, and what to do if levels are elevated.
Radon Basics in Plain English
Radon is an odorless, invisible radioactive gas produced by the breakdown of uranium in soil and rock. It can seep into buildings through cracks in the foundation or slab. Long-term exposure to elevated levels increases the risk of lung cancer, making it the second leading cause of lung cancer in the U.S. after smoking (EPA & CDC).
Because radon can’t be seen, smelled, or tasted, testing is the only way to know a property’s level.
Radon at a Glance in Tulsa County
- EPA Zone 3 (Low Potential): Tulsa County and surrounding counties (Osage, Rogers, Wagoner, Creek, Okmulgee, Pawnee, Washington) are in Zone 3, where the predicted average indoor screening level is below 2.0 pCi/L.
- Eastern Oklahoma Zone 2 Counties: A handful of counties to the east and west—Mayes, Delaware, Adair, Sequoyah, Cherokee, Cimarron, Texas, Beaver, Ellis—are Zone 2 (2.0–4.0 pCi/L).
- Analysis of CDC testing data (2008–2017) shows Tulsa County’s mean result ≈ 1.8 pCi/L across more than 300 tests, below the EPA action level.
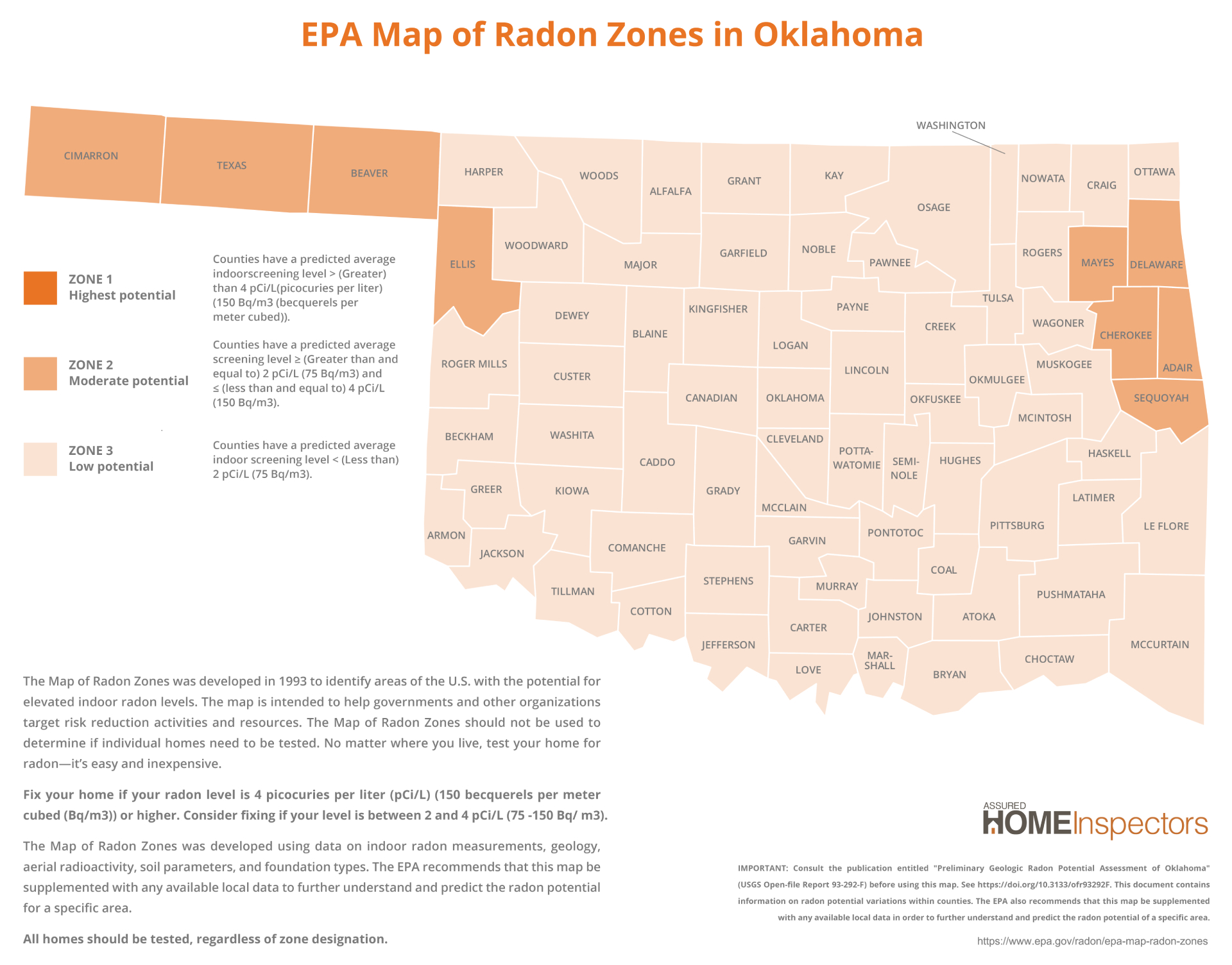
EPA Radon Zones – Oklahoma. Source: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Map shows predicted county averages; test all buildings regardless of zone. Public domain image recreated in AHI brand colors
When Radon Testing Makes Sense in Tulsa
Even in a lower-risk area, testing can be worthwhile:
- During real estate transactions (residential or commercial). EPA recommends testing every property rather than relying on neighbor results.
- If a property has a basement or lowest living area, where radon tends to be highest.
- After major renovations or HVAC changes that affect airflow.
- For peace of mind—especially for families, tenants, or employees spending time in lower-level spaces.

How AHI’s Radon Testing Works
- Short-term testing (most common in inspections)
AHI places specialized cartridges on the lowest level of your home or building for a 48-96 hour sampling period. These devices use EPA-approved liquid scintillation technology to measure radon levels with precision. After the testing period, we collect the cartridges and send them to a certified laboratory for analysis. Results are typically available within six business days, giving you timely, reliable data. - Long-term testing
For a clearer annual average, testing over 30–90 days smooths out daily and seasonal swings. - Commercial properties
AHI follows industry protocols to test multiple floors or units as required by HUD, FHA, or investor policies.
Understanding Results
| Radon Level (pCi/L) | What It Means | Recommended Action |
| 0.0 – 1.9 | Well below both WHO** and EPA* benchmarks; typical for Tulsa | No action needed Retest at sale or after major renovations. |
| 2.0 – 2.6 | Above average but below WHO’s** 2.7 reference level | Generally safe consider retesting periodically. |
| 2.7 – 3.9 | At or above WHO’s** reference level but still below EPA’s* action level | Consider mitigation Or at minimum plan for retesting, especially if time is spent in lower levels. |
| ≥ 4.0 | EPA* action level (and above WHO as well) | Mitigation strongly recommended*** Systems like sub-slab depressurization can reduce levels by 80–99%. |
*EPA action level – 4.0 pCi/L. In the U.S., the Environmental Protection Agency recommends taking corrective action if radon levels are at or above this threshold.
**WHO reference level – 2.7 pCi/L. The World Health Organization advises aiming for this lower benchmark, since health risks can occur even below the EPA’s action level.
***Effective mitigation. Proven methods such as sub-slab depressurization are non-disruptive and can typically reduce indoor radon levels by 80–99%.
Cost & Value
Given Tulsa’s generally low average, many properties will test well below action levels—but testing provides certainty and documentation.
| Testing with AHI | Mitigation (If Needed) |
| $200 add-on to any home or commercial inspection | Costs vary but are usually modest compared to the health and investment risks. |
FAQs
In Summary
Radon in Tulsa is generally a low concern compared to many parts of the U.S., but the only way to know your property’s level is to test. As a buyer, seller, or investor, a radon test during your inspection gives you clarity, protection, and peace of mind.
Add radon gas testing to your home or commercial inspection today.

